You’ve probably used AI automation today without even realizing it. Think about it:
– Your phone’s map app rerouting you around a sudden traffic jam?
– That streaming service somehow knowing you’d love a documentary about 1980s synth music?
– Your bank app freezing a fishy $700 charge before you even noticed it?
That’s AI automation quietly working in the background—learning, adapting, and making little judgment calls based on context, not just cold rules.
AI automation is happening now – in hospitals, factories, online shops, and even your home. It’s not just a distant tech wave, it’s changing things today, not just in the future.
Let’s fix that disconnect.
I’ve seen AI systems evolve from lab experiments to real partners. I’ve debugged neural networks that now help farmers predict droughts. AI automation doesn’t take over – it handles repetitive tasks, freeing us to create, connect, and make thoughtful decisions.
In this piece, we’ll ditch the fluff and get real:
1. What AI automation actually is?
2. Where it’s quietly transforming work and life—hospitals, stores, your inbox?
3. Why the fear of mass job loss misses the bigger opportunity (hint: new kinds of human work are blooming)?
4. How you can start using it, whether you’re running a team or just tired of manual chores?
5. ‘Spot the AI‘ Quiz to guess which daily tasks involve AI automation. (Bonus)
Ready to meet the invisible engine shaping your days? Let’s dig in.
Spot the AI Quiz
Guess which daily tasks involve AI automation
What Exactly Is AI Automation? (And How Is It Different?)
Here’s a truth that surprises people: Automation doesn’t always think. And AI doesn’t always act.
For decades, automation meant rigid, pre-programmed instructions like an Excel macro that flawlessly formats a spreadsheet… until you swap two columns. Then? It’s chaos. It’s fast, sure but fragile. Break its rules, and it breaks.
AI automation flips that script. It’s what happens when you teach machines to learn from the messiness of life. Instead of just following “if this, then that” commands, these systems:
– Spot patterns in oceans of data (like which emails you ignore vs. rush to open),
– Get smarter with practice (ever notice how your voice assistant understands your mumbled “remind me…” better than it did a year ago?),
– Navigate gray areas—language, blurry images, unpredictable workflows—without tripping,
– Make judgment calls based on the situation, not just code.
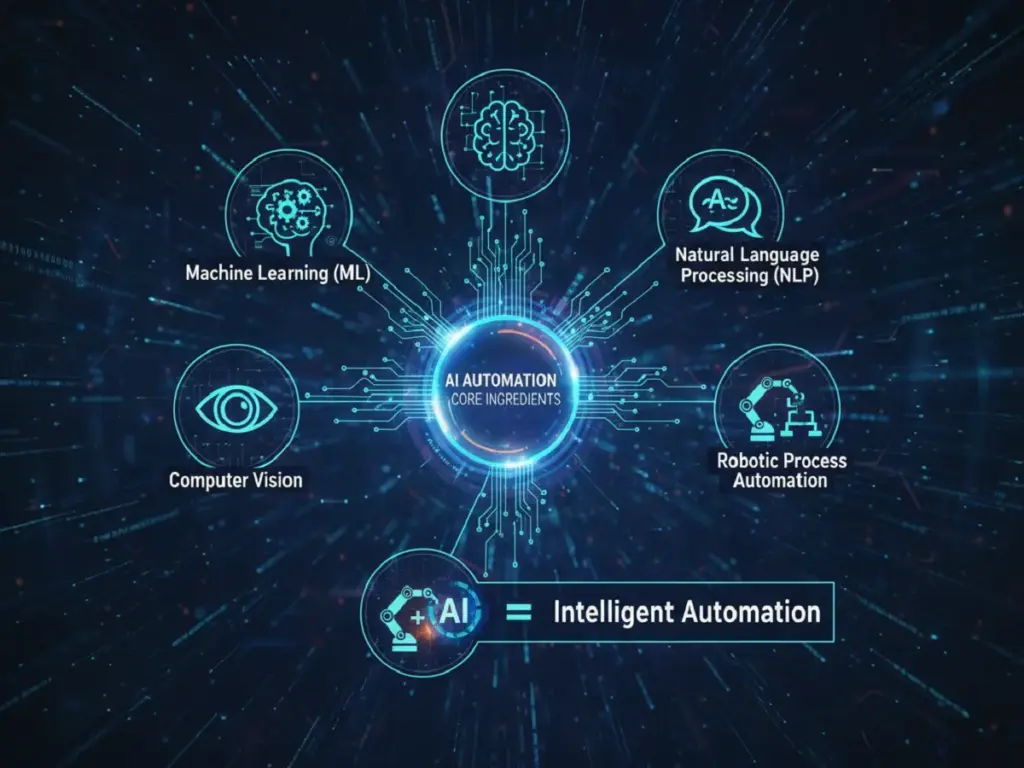
So what’s under the hood? Four key players:
1. Machine Learning (ML): The Curious Learner
This is the engine that teaches itself by example. Feed it a million cat photos, and it’ll recognize your tabby crossing the street—even in fog. That spam filter that now catches phishing emails disguised as your utility bill? ML noticed the tiny writing quirks humans miss. It doesn’t just execute; it evolves.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP): The Listener
Ever typed “ugh, my flight got canceled—help!” into a chatbot and had it actually get your frustration? That’s NLP. It’s teaching machines to parse not just words, but tone, urgency, even sarcasm. (Still a work in progress, but getting scarily good.)
3. Computer Vision: The Observer
This gives AI eyes that understand. It’s not just seeing pixels—it’s spotting a hairline crack in a bridge weld, recognizing your face in a crowd (with consent, hopefully), or knowing a tomato is ripe by its color gradient. Think of it as pattern recognition with depth perception.
4. RPA + AI = The Upgraded Assistant
Old-school RPA was the ultimate button-pusher: copying data, filling forms, clicking “send.” Reliable but mindless.
Add AI? Suddenly it’s reading your handwritten invoice, figuring out which department owes what, spotting a typo, and learning from your corrections. It’s automation that doesn’t just repeat; it comprehends.
The real game-changer? Context.
Traditional automation: “If payment > $10k, send to finance.”
AI automation: “This vendor usually invoices on Tuesdays, but this one’s flagged as high-risk, came at 2 a.m., and the total is just under your threshold—maybe flag it gently?”
It’s the difference between a calculator and a colleague who whispers, “Hey, double-check this—it feels off.”
AI vs Automation: Key Differences
Traditional automation is a train on rails. AI automation is a self-driving car: it navigates traffic, reroutes around accidents, and even parks itself by sensing, learning, and deciding.
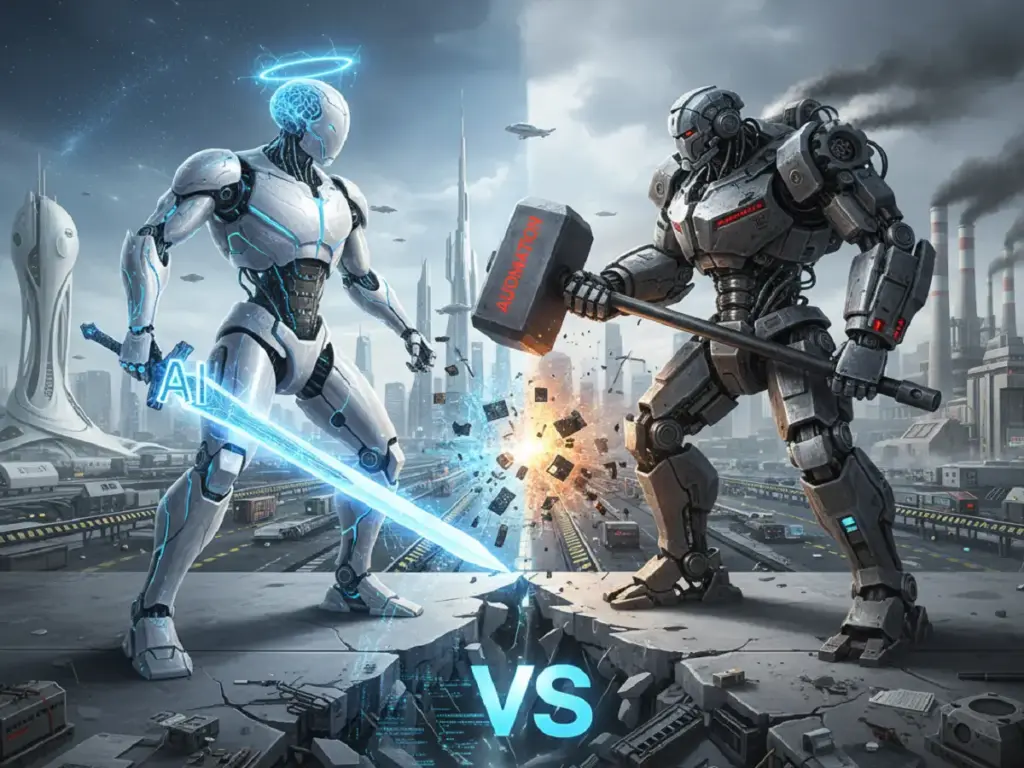

| Feature | Traditional Automation | AI Automation |
| Logic Basis | Fixed rules (if/then) | Learns from data |
| Data Handling | Structured only (spreadsheets, databases) | Structured + unstructured (emails, images, voice) |
| Adaptability | Breaks when inputs change | Improves with new data |
| Decision Depth | Binary choices | Probabilistic, contextual judgments |
| Human Intervention | High (when rules fail) | Low (self-correcting over time) |
| Example | Factory arm welding same car part | AI vision inspecting welds for micro-cracks across varying models |
Real-World Use Cases: AI Automation in Action
Let’s move from theory to practice. Here’s where AI automation is already changing lives—yours included. Each example includes a Before vs. After snapshot to ground the transformation.
A. Healthcare: Saving Lives with Smarter Systems
Before:
A radiologist spends hours reviewing hundreds of chest X-rays, often getting tired and prone to missing things. Scheduling surgeries and ER beds still relies on manual spreadsheets and making educated guesses.
After:
An AI triage system flags 15 abnormal scans overnight. It prioritizes them for the morning shift. A predictive model uses admission trends, weather, and flu data. This alerts the hospital to reserve 12 extra ICU beds for next Tuesday.
How It Works:
– AI Triage: Tools like Babylon or Ada ask symptom questions like a clinician. They prioritize cases, filtering low-risk ones so doctors focus on critical care, not paperwork.
– Medical Imaging: Deep learning analyzes scans, spotting tumors or bleeds as accurately as human specialists, often faster. AI-powered eye exams in rural India catch diabetic blindness early where doctors are scarce.
– Predictive Allocation: Johns Hopkins Hospital uses AI to predict ER needs. It analyzes ER arrivals, flu forecasts, and event data. As a result, ER wait times dropped by 18%. The hospital pre-allocates beds, staff, and supplies accordingly.
This isn’t about replacing doctors. It’s about giving them superpowers: time, clarity, and foresight.
B. Retail & E-Commerce: The Invisible Personal Shopper
Before:
You browse a website. Static recommendations (“Customers who bought X also bought Y”) appear, regardless of whether you’re shopping for socks or a anniversary gift.
After:
You glance at a jacket on your lunch break. That evening, your favorite app shows matching scarves, suggests a size based on past returns, and offers a dynamic discount because inventory is high and rain is forecast tomorrow.
How It Works:
– Dynamic Pricing: Airlines first did it. Now Amazon changes prices by the minute based on demand, rivals, and stock. It’s capitalism that’s always optimizing.
– Inventory Forecasting: Zara’s secret weapon? AI that chews sales data, Instagram trends, weather, and local concerts to predict demand per SKU. Result: designs hit stores in 14 days, not months. Less waste, more relevance—like a psychic buyer who actually delivers.
– Hyper-Personalization: NLP analyzes reviews like “too tight” and “great for hiking”. Computer vision tracks the styles you view. Reinforcement learning makes the next recommendation. This leads to 35% of Amazon’s sales.
The store knows you better than the clerk ever did—without judgment or coffee breaks.
C. Manufacturing: The Smart Factory Floor
Before:
Machines run until they fail. Quality control means human inspectors staring at conveyor belts for hours, missing micro-cracks. Supply chains break from minor delays.
After:
Vibration sensors predict motor bearing wear 72 hours ahead. AI cameras scan bottles, rejecting those with hairline fractures. Autonomous robots reroute deliveries around delayed pallets.
How It Works:
– Predictive Maintenance: Sensors collect temperature, noise, and vibration data. ML models spot anomalies—like a bearing’s “cough” before it fails. Siemens reduced unplanned downtime by 50% in one plant.
– Computer Vision QC: Unlike humans, AI doesn’t get tired. It spots misaligned labels, subtle color variations, or microscopic defects in silicon wafers. Foxconn uses it to inspect iPhone casings at scale.
– Warehouse Logistics: Amazon’s Kiva robots (now evolved) slashed “click-to-ship” time from 60–75 minutes to under 15. AI plans optimal routes, balances workloads, and even predicts which items will sell fastest after a TikTok trend.
The factory isn’t just automated. It’s self-aware.
D. Finance: From Fraud Detection to Financial Advice
Before:
Fraud alerts trigger after your card is already maxed out. Loan officers rely on credit scores that miss context—like a nurse’s steady income despite pandemic gaps.
After:
Your bank blocks a $900 “electronics” charge in Tokyo while you’re at lunch in Chicago because the AI noticed: no travel alert, unusual merchant category, and your phone’s GPS says “home.” Seconds later, you get a push notification: “Suspicious? Tap NO to block.”
How It Works:
– Fraud Detection: Mastercard’s AI systems analyze billions of transactions in real time. They spot subtle anomalies, like a sudden luxury purchase after months of buying groceries. They also learn new scam patterns every hour from global data.
– AI-Driven Underwriting: Upstart’s ML considers education, job stability, and cash flow to identify trustworthy borrowers overlooked by traditional systems. This approach approves 27% more underserved groups with lower default rates.
– Robo-Advisors: Betterment and Wealthfront build portfolios with machine precision, charging 0.25% vs. humans’ 1%+. They don’t sleep, panic-sell, or chase hype. Just steady, emotion-free rebalancing like a financial advisor distilled to its most disciplined, tireless core.
Finance isn’t cold anymore. It’s contextual.
E. Everyday Life: The AI in Your Pocket
Before:
You set your thermostat manually. Missed calls pile up. Spam floods your inbox, and you delete Nigerian prince emails weekly.
After:
Your thermostat pre-cools the house before you arrive, having learned your commute. Your voice assistant reschedules a missed meeting by parsing your email and calendar. Spam filters catch a new phishing attempt mimicking your bank—before you open it.
How It Works:
– Smart Homes: Nest doesn’t just “schedule.” It sees you lower the heat at 10 p.m. every Tuesday. It links this with weather and occupancy sensors. Then, it creates a personalized thermal model. It’s not just automation; it’s accommodation.
– Voice Assistants (Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant): NLP + task automation. “Add milk to my shopping list” → syncs to your phone, partner’s device, and even the grocery store’s app for pickup.
– Email Filters: Modern spam systems (like Google’s TensorFlow-powered Gmail filters) don’t just block known bad senders. They analyze writing style, embedded links, sender reputation, and timing—catching “urgent wire transfer” scams that fooled humans for years.
> Your life isn’t just digitized. It’s being quietly, thoughtfully orchestrated—by systems learning you.
The Human Side: Myths, Fears, and Opportunities
Let’s address the elephant in the room: “Is AI coming for my job?” The short answer: Not if you redefine what “your job” means.
Myth: “AI Automation = Mass Job Loss”
History offers a counter-narrative. ATMs didn’t eliminate bank tellers—they shifted their role from cash counting to relationship advising. Teller numbers increased post-ATM as banks opened more branches.
Similarly, AI automation displaces tasks, not entire humans. A 2023 MIT study found that only 23% of worker tasks in the U.S. are cost-effective to automate today—because so much work requires judgment, empathy, or physical dexterity AI can’t yet replicate.
Reality: Augmentation, Not Replacement
– Radiologists become “diagnostic team leads,” overseeing AI suggestions and focusing on complex cases and patient communication.
– Customer service reps handle only escalated issues—empowered by AI summaries of prior interactions, purchase history, and emotional tone analysis.
– Farmers use AI to monitor crop health via drone imagery, then decide which fields to water, harvest, or treat—blending data with generational intuition.
Opportunity: The Rise of the AI Collaborator
Forget “robots stealing jobs”—new human roles are blooming where intuition meets AI’s raw power. These aren’t just tech gigs; they’re bridges between complexity and clarity:
Prompt Engineers: AI Whisperers craft clear instructions to get reliable AI outputs. They turn vague requests into precise prompts, no coding needed.
Automation Trainers: Taskmasters teach AI your organization’s quirks. They embed domain-specific logic so AI adapts to your workflow.
AI Auditors: Bias detectives check algorithms for fairness issues, like why a loan model rejects night-shift nurses more often. They demand transparency to prevent AI from repeating human mistakes at scale.
Human-AI Experience Designers: Tone Tamers make tools helpful, not annoying. They use psychology and UX to make AI feel like a trusted colleague, not a clumsy intern.
Ethical Considerations: The Dark Corners
AI automation isn’t neutral. It reflects our world, flaws and all.
- Bias in, bias out: An HR automation tool trained on past resumes may undervalue women in tech or Black applicants from underfunded schools.
- Transparency Black Boxes: Deep learning models often can’t explain why they flagged a transaction or denied parole. This lack of clarity erodes trust.
- Accountability Gaps: If an autonomous vehicle crashes, who is responsible? Is it the programmer, the sensor maker, or the AI? (Spoiler: Courts are still figuring this out.)
The solution isn’t to stop progress. Instead, we need guardrails. Here’s how:
- Use diverse training data.
- Create explainable AI (XAI) interfaces.
- Implement human override protocols.
- Conduct ongoing audits.
Getting Started: How Businesses (and Individuals) Can Leverage AI Automation
You don’t need a PhD or a billion-dollar budget. You need curiosity, clarity, and a starting point.
1. No-Code AI Tools
Platforms like Make.com, Zapier AI Actions, Lobe (by Microsoft), or Hugging Face let you connect AI models to workflows with drag-and-drop. Upload customer feedback → get sentiment summaries. Connect your calendar → auto-draft meeting recaps.
2. AI-Enhanced SaaS
Your CRM, email marketing, or accounting software likely has AI features already. Turn them on.
– HubSpot: AI suggests email send times per contact.
– QuickBooks: Auto-categorizes expenses by scanning receipts.
– Canva: Generates social posts from a product photo and a goal (“drive sales”).
3. Start Small, Scale Smart
Don’t “AI-ify” your entire business. Pick one high-volume, low-risk task:
– Sorting customer support tickets
– Generating job descriptions
– Summarizing meeting transcripts
For Individuals: You’re Already Using It—Level Up
– Use AI as a thought partner: Ask ChatGPT or Claude to “summarize this 30-page report in bullet points for a non-expert audience” or “suggest 5 questions I should ask before investing in solar panels.”
– Automate your digital clutter: Tools like Sanebox use AI to filter low-priority emails. Rewind.ai captures everything you see, say, or type—then lets you search your past like Google.
– Build one micro-automation: Connect your smart lights to sunset times via IFTTT + AI weather forecast. Tiny wins breed confidence.
You don’t need to build the AI. You just need to know how to steer it.
Conclusion: Embracing the Automated Future—Thoughtfully
AI automation is not a utopia. Nor is it a dystopian job thief. It’s a tool—like electricity, the internet, or the spreadsheet. Initially feared, eventually indispensable.
What separates hype from impact is intention. When deployed ethically, transparently, and with human oversight, AI automation doesn’t depersonalize the world; it reclaims time for the things that matter.
- A nurse spends less charting, more holding hands.
- A teacher automates grading quizzes, freeing evenings for student mentorship.
- A small business owner competes with giants—not by hiring 50 people, but by arming 5 with AI superpowers.
The most successful future won’t belong to those who fear AI, or worship it but to those who partner with it.